#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
//非递归查找
int HalfFind(int arr[],int size,int key)
{
int low=0;
int high=size-1;
int mid=0;
int result=-1;
while (low<=high)
{ mid=(low+high)/2;
if(key==arr[mid])
{
result=arr[mid];
break;
}
else if(key>mid)
low=mid+1;
else
high=mid-1;
}
return result;
}
//递归查找
int HalfFind(int arr[],int low,int high,int key)
{
if(low<=high)
{
int mid=(low+high)/2;
if(arr[mid]==key)
{
return arr[mid];
}
else if(key>arr[mid])
HalfFind(arr,mid+1,high,key);
else
HalfFind(arr,low,mid-1,key);
}
else
return -1;
}
int main(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int test[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
cout<<HalfFind(test,10,1)<<endl;
cout<<HalfFind(test,0,9,1)<<endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}
作者归档:244128133
c++实现红黑树
本代码来自互联网,如有侵权,立删.
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#define BLACK 0
#define RED 1
#define NULL 0
typedef int BOOL;
typedef struct RBTreeNode
{
int key;
int color;
struct RBTreeNode *parent, *left, *right;
RBTreeNode(){}
RBTreeNode(int k):key(k){ // 创建新结点默认颜色为红色
color = RED;
parent = NULL;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;}
}RBTree, RBTreeNode;
class CRBTree
{
public:
CRBTree();
virtual ~CRBTree();
void RB_InitLeafNode();
BOOL RB_Insert(int keyVal);
BOOL RB_Delete(int keyVal);
RBTreeNode *RB_Find(int keyVal);
void RB_Print();
int RB_GetSize()const { return m_Size; }
private:
void RB_Insert_FixedUp(RBTreeNode *&pNode);
void RB_Del_FixedUp(RBTreeNode *&pNode);
void RB_Left_Rotate(RBTreeNode *&pNode);
void RB_Right_Rotate(RBTreeNode *&pNode);
void RB_Print(RBTreeNode *&pNode);
void RB_SwapTwoNodes(RBTreeNode *&pNode1, RBTreeNode *&pNode2);
void RB_EmptyTree(RBTreeNode *&pNode);
private:
RBTree *m_root; //根结点
RBTreeNode *m_NIL; // 空结点
int m_Size;
};
using namespace std;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// Construction/Destruction
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// 构造函数
CRBTree::CRBTree()
{
m_root = m_NIL = NULL;
m_Size = 0;
}
// 析构函数
CRBTree::~CRBTree()
{
RB_EmptyTree(m_root);
delete m_NIL;
m_root = m_NIL = NULL;
cout << "Empty the tree!\n";
}
// 初始化叶子结点
void CRBTree::RB_InitLeafNode()
{
m_root = new RBTree(-1);
m_NIL = new RBTreeNode(-1);
m_NIL->color = BLACK; // 叶子结点颜色都为黑色
m_NIL->parent = NULL;
m_NIL->left = m_NIL->right = NULL;
m_root = m_NIL;
m_root->parent = m_NIL;
}
// 插入树结点
BOOL CRBTree::RB_Insert( int keyVal )
{
RBTreeNode *pNewNode = new RBTreeNode(keyVal);
pNewNode->left = m_NIL;
pNewNode->right = m_NIL;
RBTreeNode *pNode = m_root;
RBTreeNode *pPreNode = m_NIL;
while(pNode != m_NIL) // 树不为空
{
pPreNode = pNode;
if (keyVal < pNode->key)
{
pNode = pNode->left;
}
else if (keyVal > pNode->key)
{
pNode = pNode->right;
}
else{
delete pNewNode;
return 0;
}
}
pNewNode->parent = pPreNode;
if (pPreNode == m_NIL) // 树为空
{
pNewNode->color = BLACK;
m_root = pNewNode;
}
else
{
if (keyVal < pPreNode->key)
{
pPreNode->left = pNewNode;
}
else
pPreNode->right = pNewNode;
}
m_Size++;
cout << "Insert "<< m_Size << " node: " << keyVal << " succeeded!\n";
RB_Insert_FixedUp(pNewNode);
return 1;
}
// 删除树结点
BOOL CRBTree::RB_Delete( int keyVal )
{
RBTreeNode *pDelNode, *pPreNode = m_NIL;
if (m_root == m_NIL)
{
return 0;
}
// pDelNode = m_root;
// while(pDelNode != m_NIL)
// {
// if (keyVal < pDelNode->key)
// {
// pPreNode = pDelNode;
// pDelNode = pDelNode->left;
// }
// else if (keyVal > pDelNode->key)
// {
// pPreNode = pDelNode;
// pDelNode = pDelNode->right;
// }
// else
// break;
// }
pDelNode = RB_Find(keyVal);
if (pDelNode == NULL)
{
return 0; // 没有此结点
}
pPreNode = pDelNode->parent;
//从该结点的左子树找出最大的结点或从右子树找出最小的结点, 两者的值进行替换
RBTreeNode *pTemp;
RBTreeNode *pDelChild;
if (pDelNode->left != m_NIL && pDelNode->right != m_NIL)
{ // 有两个子结点,查找左子树
pTemp = pDelNode->left;
while(pTemp->right != m_NIL)
{
pTemp = pTemp->right;
}
RB_SwapTwoNodes(pTemp, pDelNode);
pDelChild = pTemp->left;
pDelChild->parent = pTemp->parent;
if (pTemp->parent->left == pTemp)
{
pTemp->parent->left = pDelChild;
}
else
pTemp->parent->right = pDelChild;
}
else if (pDelNode->left == m_NIL && pDelNode->right == m_NIL)
{ // 要删除的结点是叶子结点
if (pPreNode == m_NIL)
{
delete m_root;
m_root = m_NIL;
m_Size--;
return 1;
}
else
{
if (pDelNode == pDelNode->parent->left)
{
pPreNode->left = m_NIL;
}
else
pPreNode->right = m_NIL;
pDelChild = m_NIL;
pDelChild->parent = pDelNode->parent;
pTemp = pDelNode;
}
}
else // 有一个子结点
{
if (pDelNode->left != m_NIL)
{
pDelChild = pDelNode->left;
}
else
{
pDelChild = pDelNode->right;
}
if (pDelChild == pPreNode->left)
{
pDelChild->parent = pPreNode;
pPreNode->left = pDelChild;
}
else
{
pDelChild->parent = pPreNode;
pPreNode->right = pDelChild;
}
pTemp = pDelNode;
}
if (pTemp->color == BLACK)
{
RB_Del_FixedUp(pDelChild);
}
cout << "Deleted node: " << pTemp->key << endl;
delete pTemp;
m_Size--;
return 1;
}
// 查找指定结点,成功 放回该结点,否则返回NULL
RBTreeNode * CRBTree::RB_Find( int keyVal )
{
RBTreeNode *pNode;
if (m_root == m_NIL)
{
return NULL;
}
pNode = m_root;
while(pNode != m_NIL)
{
if (keyVal < pNode->key)
{
pNode = pNode->left;
}
else if (keyVal > pNode->key)
{
pNode = pNode->right;
}
else{
cout << "Find node: " << keyVal << "succeeded!\n";
return pNode;
}
}
return NULL;
}
// 插入结点后形成的新结构不满足红黑树性质和对其进行处理
void CRBTree::RB_Insert_FixedUp( RBTreeNode *&pNode )
{
while (pNode->parent->color == RED)
{
RBTreeNode *pNodeParent = pNode->parent;
RBTreeNode *pNodePaBro;
if (pNodeParent->parent->left == pNodeParent)
pNodePaBro = pNodeParent->parent->right;
else
pNodePaBro = pNodeParent->parent->left;
if (pNodePaBro->color == RED)
{ // 父结点和叔结点都是红色 ==>> 父--黑 叔--黑 祖父--红
pNodeParent->color = BLACK;
pNodePaBro->color = BLACK;
pNodeParent->parent->color = RED;
pNode = pNode->parent->parent;
if (pNode == m_NIL)
{
m_root->color = BLACK;
return ;
}
}
/// 红父 黑叔结点 或者没有叔结点
else if(pNodeParent->parent->left == pNodeParent && pNodeParent->left == pNode)
{
pNodeParent->color = BLACK;
pNodeParent->parent->color = RED;
cout<<"右旋转"<<endl;
RB_Right_Rotate(pNode->parent->parent);
break;
}
else if (pNodeParent->parent->left == pNodeParent && pNodeParent->right == pNode)
{
pNode = pNode->parent;
RB_Left_Rotate(pNode);
}
else if (pNodeParent->parent->right == pNodeParent && pNodeParent->left == pNode)
{
pNode = pNode->parent;
RB_Right_Rotate(pNode);
}
else
{
pNodeParent->color = BLACK;
pNodeParent->parent->color = RED;
RB_Left_Rotate(pNode->parent->parent);
break;
}
}// while
m_root->color = BLACK;
}
// 删除结点后形成的新结构不满足红黑树性质和对其进行处理
void CRBTree::RB_Del_FixedUp( RBTreeNode *&pNode )
{
int nLRFlag;
RBTreeNode *pBroNode;
while(pNode != m_root && pNode->color == BLACK)
{
if (pNode->parent->left == pNode)
{
nLRFlag = 0;
pBroNode = pNode->parent->right;
}
else
{
nLRFlag = 1;
pBroNode = pNode->parent->left;
}
//1 父-red 无兄 子-red ==>> 子-black
//2 父-black 兄-red ==>> 父-red 兄-black 旋转父结点
if (pBroNode->color == RED)
{
pNode->parent->color = BLACK;
pBroNode->color = BLACK;
if (nLRFlag == 0)
{
RB_Left_Rotate(pNode->parent);
}
else
RB_Right_Rotate(pNode->parent);
}
//3 兄-black 两黑侄 ==>> 兄=红 子=黑 红父=黑 往上遍历(黑父)
else if (pBroNode->left->color == BLACK && pBroNode->right->color == BLACK)
{
pNode->color = BLACK;
pBroNode->color = RED;
pNode->parent->color = BLACK;
pNode = pNode->parent; // 往上遍历
}
//4 兄-black 左黑侄右红侄 ==>> 兄=父色 父=黑 侄=黑 (子=黑) 左旋转父节点
else if (pBroNode->left->color == BLACK && pBroNode->right->color == RED)
{
if (nLRFlag == 0)
{
pBroNode->color = pNode->parent->color;
pNode->parent->color = BLACK;
pNode->color = BLACK;
pBroNode->right->color = BLACK;
RB_Left_Rotate(pNode->parent);
break;
}
else
{
RBTreeNode *pPa = pNode->parent;
pBroNode->left->color = pNode->parent->color;
pNode->parent->color = BLACK;
RB_Left_Rotate(pBroNode);
RB_Right_Rotate(pPa);
break;
}
}
//5 兄-black 左红侄右黑侄 ==>> 侄=父色 父=黑 右旋转兄 左旋转父
else if (pBroNode->left->color == RED && pBroNode->right->color == BLACK)
{
if (nLRFlag == 0)
{
RBTreeNode *pPa = pNode->parent;
pBroNode->left->color = pNode->parent->color;
pNode->parent->color = BLACK;
RB_Right_Rotate(pBroNode);
RB_Left_Rotate(pPa);
break;
}
else
{
pBroNode->color = pNode->parent->color;
pNode->parent->color = BLACK;
pNode->color = BLACK;
pBroNode->right->color = BLACK;
RB_Right_Rotate(pNode->parent);
break;
}
}
else //两红侄的情况 转换成一黑一红的情况
{
if (nLRFlag == 0)
{
pBroNode->left->color = BLACK;
}
else
{
pBroNode->right->color = BLACK;
}
}
}
pNode->color = BLACK; //子 ==> black
return;
}
// 左旋处理
void CRBTree::RB_Left_Rotate( RBTreeNode *&pNode )
{
RBTreeNode *pNodeA = pNode->parent;
RBTreeNode *pNodeB = pNode->right;
pNode->right = pNodeB->left;
pNodeB->left->parent = pNode;
pNodeB->left = pNode;
pNode->parent = pNodeB;
if (pNode == pNodeA->left)
{ // 父子不同边
pNodeA->left = pNodeB;
pNodeB->parent = pNodeA;
}
else if (pNode ==pNodeA->right)
{
pNodeA->right = pNodeB;
pNodeB->parent = pNodeA;
}
else // m_root == m_NIL
{
if (pNodeA == m_NIL)
{ // pNode 原本为根结点
pNodeB->parent = m_NIL;
m_root = pNodeB;
}
}
cout << "RB_Left_Rotate()\n";
}
// 右旋处理函数
void CRBTree::RB_Right_Rotate( RBTreeNode *&pNode )
{
RBTreeNode *pNodeA = pNode->parent;
RBTreeNode *pNodeB = pNode->left;
pNode->left = pNodeB->right;
pNodeB->right->parent = pNode;
pNodeB->right = pNode;
pNode->parent = pNodeB;
if (pNode == pNodeA->right)
{ // 父子不同边
pNodeA->right = pNodeB;
pNodeB->parent = pNodeA;
cout<<"父子不同边"<<endl;
}
else if (pNode==pNodeA->left)
{
pNodeA->left = pNodeB;
pNodeB->parent = pNodeA;
}
else // m_root == m_NIL
{
if (pNodeA == m_NIL)
{ // pNodeA 原本为父结点
pNodeB->parent = m_NIL;
m_root = pNodeB;
}
}
cout << "RB_Right_Rotate()\n";
}
void CRBTree::RB_Print()
{
if (m_root == m_NIL)
{
cout << "树为空!\n";
return ;
}
RB_Print(m_root);
cout << endl;
}
void CRBTree::RB_Print( RBTreeNode *&pNode )
{
if (pNode != m_NIL)
{
cout << pNode->key << "(" << pNode->color << ") ";
RB_Print(pNode->left);
RB_Print(pNode->right);
}
}
void CRBTree::RB_SwapTwoNodes( RBTreeNode *&pNode1, RBTreeNode *&pNode2 )
{
int t = pNode1->key;
pNode1->key = pNode2->key;
pNode2->key = t;
}
void CRBTree::RB_EmptyTree( RBTreeNode *&pNode )
{
if (pNode != m_NIL)
{
RB_EmptyTree(pNode->left);
RB_EmptyTree(pNode->right);
delete pNode;
}
}
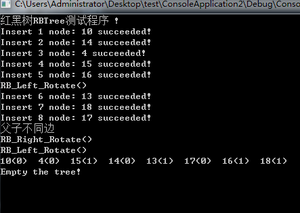
void Fun_Test()
{
CRBTree tree;
tree.RB_InitLeafNode();
tree.RB_Insert(10);
tree.RB_Insert(14);
tree.RB_Insert(4);
tree.RB_Insert(15);
tree.RB_Insert(16);
tree.RB_Insert(13);
tree.RB_Insert(18);
tree.RB_Insert(17);
tree.RB_Print();
// tree.RB_Delete(14);
// tree.RB_Delete(10);
// Sleep(1000);
// tree.RB_Print();
}
int main()
{
cout << "红黑树RBTree测试程序 !\n";
Fun_Test();
getchar();
return 0;
}
c++实现二叉树的创建和遍历
最近想复习一下数据结构和算法,所以就写了一个二叉树的创建和遍历
// test2.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct tree//树结构体
{
int data;
tree *left,*right;
};
class Ctree
{
public:
static int n;
static int m;
tree *root;
Ctree()
{
root=NULL;
}
void CreateTreeNode(int a);//创建树节点;
int Sum(tree*);
void PreOrder(tree*);
void MedialOrder(tree*);
void BackOrder(tree*);
};
int Ctree::m=0;
int Ctree::n=0;
void Ctree::CreateTreeNode(int data)
{
tree *newNode=new tree;
newNode->data=data;
newNode->right=newNode->left=NULL;
if(root==NULL)
root=newNode;
else
{
tree *tail;
tree *cur=root;
while(cur!=NULL)
{ tail=cur;
if(data<cur->data)
cur=cur->left;
else
cur=cur->right;
}
if(data<tail->data)
tail->left=newNode;
else
tail->right=newNode;
}
}
int Ctree::Sum(tree *p)//计算结点数
{
if(p==NULL)
return 0;
else
return Sum(p->left)+Sum(p->right)+1;
}
void Ctree::PreOrder(tree *p)//先序遍历;
{
if(p!=NULL)
{
cout<<p->data<<endl;
PreOrder(p->left);
PreOrder(p->right);
}
}
void Ctree::MedialOrder(tree*p)//中序遍历
{
if(p!=NULL)
{
MedialOrder(p->left);
cout<<p->data<<endl;
MedialOrder(p->right);
}
}
void Ctree::BackOrder(tree *p)//后序遍历
{
if(p!=NULL)
{
BackOrder(p->left);
BackOrder(p->right);
cout<<p->data<<endl;
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
Ctree *T=new Ctree();
T->CreateTreeNode(10);//根结点
T->CreateTreeNode(7);
T->CreateTreeNode(8);
T->CreateTreeNode(11);
T->CreateTreeNode(9);
T->CreateTreeNode(6);
cout<<"结点数:"<<T->Sum(T->root)<<endl;
cout<<"先序遍历:"<<endl;
T->PreOrder(T->root);
cout<<"中序遍历:"<<endl;
T->MedialOrder(T->root);
cout<<"后序遍历:"<<endl;
T->BackOrder(T->root);
getchar();
return 0;
}
输出结果如下:
c#异步委托的使用
创建线程的一种简单方式是定义一个委托,并异步调用它。 委托是方法的类型安全的引用。Delegate类 还支持异步地调用方法。在后台,Delegate类会创建一个执行任务的线程。
接下来定义一个方法,使用委托异步调用(开启一个线程去执行这个方法)
static int TakesAWhile(int data,int ms){
Console.WriteLine("TakesAWhile started!");
Thread.Sleep(ms);//程序运行到这里的时候会暂停ms毫秒,然后继续运行下一语句
Console.WriteLine("TakesAWhile completed");
return ++data;
}
public delegate int TakesAWhileDelegate(int data,int ms);// 声明委托
static void Main(){
TakesAWhileDelegate d1 = TakesAWhile;
IAsyncResult ar = d1.BeginInvoke(1,3000,null,null);
while(ar.IsCompleted ==false ){
Console.Write(".");
Thread.Sleep(50);
}
int result = d1.EndInvoke(ar);
Console.WriteLine("Res:"+result);
}
C#里面的反射和特性
在C#中反射的实现是使用System.Type类实现的.
System.Type类部分成员
成员 成员类型 描述
Name 属性 返回类型的名字
Namespace 属性 返回包含类型声明的命名空间
Assembly 属性 返回声明类型的程序集。
GetFields 方法 返回类型的字段列表
GetProperties 方法 返回类型的属性列表
GetMethods 方法 返回类型的方法列表
获取Type对象有两种方式
1,Type t = myInstance.GetType();//通过类的实例来获取Type对象
在object类有一个GetType的方法,返回Type对象,因为所有类都是从object继承的,所以我们可以在任何类型上使用GetType()来获取它的Type对象
2,Type t = typeof(ClassName);//直接通过typeof运算符和类名获取Type对象
获取里面的属性
FieldInfo[] fi = t.GetFields();
foreach(FieldInfo f in fi){
Console.WriteLine(f.Name+” “);
}
Assembly类在System.Reflection命名空间中定义,它允许访问给定程序集的元数据,它也包含了可以加载和执行程序集。
如何加载程序集?
1,Assembly assembly1 = Assembly.Load(“SomeAssembly”);根据程序集的名字加载程序集,它会在本地目录和全局程序集缓存目录查找符合名字的程序集。
2,Assembly assembly2 = Assembly.LoadFrom(@”c:\xx\xx\xx\SomeAssembly.dll”)//这里的参数是程序集的完整路径名,它不会在其他位置搜索。
1,获取程序集的全名 string name = assembly1.FullName;
2,遍历程序集中定义的类型 Type[] types = theAssembly.GetTypes();
foreach(Type definedType in types){
//
}
3,遍历程序集中定义的所有特性(稍后介绍)
Attribute[] definedAttributes = Attribute.GetCustomAttributes(someAssembly);
什么是特性?
特性(attribute)是一种允许我们向程序的程序集增加元数据的语言结构。它是用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类。
将应用了特性的程序结构叫做目标
设计用来获取和使用元数据的程序(对象浏览器)叫做特性的消费者
.NET预定了很多特性,我们也可以声明自定义特性
应用特性
先看看如何使用特性。特性的目的是告诉编译器把程序结构的某组元数据嵌入程序集。我们可以通过把特性应用到结构来实现。
案例1
[Serializable] //特性
public class MyClass{
// …
}
案例2
[MyAttribute(“Simple class”,”Version 3.57″)] //带有参数的特性
public class MyClass{
//…
}
Obsolete特性->.NET预定义特性
一个程序可能在其生命周期中经历多次发布,而且很可能延续多年。在程序生命周期的后半部分,程序员经常需要编写类似功能的新方法替换老方法。处于多种原因,你可能不再使用哪些调用过时的旧方法的老代码。而只想用新编写的代码调用新方法。旧的方法不能删除,因为有些旧代码也使用的旧方法,那么如何提示程序员使用新代码呢?可以使用Obsolete特性将程序结构标注为过期的,并且在代码编译时,显示有用的警告信息。
class Program{
[Obsolete(“Use method SuperPrintOut”)] //将特性应用到方法
static void PrintOut(string str){
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
[Obsolete(“Use method SuperPrintOut”,true)]//这个特性的第二个参数表示是是否应该标记为错误,而不仅仅是警告。
static void PrintOut(string str){
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
static void Main(string[] args){
PrintOut(“Start of Main”);
}
}
Conditional特性
Conditional特性允许我们包括或取消特定方法的所有调用。为方法声明应用Conditional特性并把编译符作为参数来使用。
定义方法的CIL代码本身总是会包含在程序集中,只是调用代码会被插入或忽略。
#define DoTrace
class Program{
[Conditional(“DoTrace”)]
static void TraceMessage(string str){
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
static void Main(){
TraceMessage(“Start of Main”);
Console.WriteLine(“Doing work in Main.”)
TraceMessage(“End of Main”);
}
}
调用者信息特性
调用者信息特性可以访问文件路径,代码行数,调用成员的名称等源代码信息。
public static void PrintOut(string message,[CallerFilePath] string filename=””,[CallerLineNumber]int lineNumber = 0,[CallerMemberName]string callingMember=””){
Console.WriteLine(“Message:”+message);
Console.WriteLine(“Line :”+lineNumber);
Console.WriteLine(“Called from:”+callingMember);
Console.WriteLine(“Message :”+message);
}
DebuggerStepThrough特性
我们在单步调试代码的时候,常常希望调试器不要进入某些方法。我们只想执行该方法,然后继续调试下一行。DebuggerStepThrough特性告诉调试器在执行目标代码时不要进入该方法调试。有些方法小并且毫无疑问是正确的,在调试时对其反复单步调试只能徒增烦恼。要小心使用该特性,不要排除了可能出现bug的代码。
该特性位于System.Diagnostics命名空间下
该特性可用于类,结构,构造方法,方法或访问器
class Program{
int _x=1;
int X{
get{return _x;};
[DebuggerStepThrough]
set{
_x=_x*2;
_x+=value;
}
}
public int Y{get;set;}
[DebuggerStepThrough]
void IncrementFields(){
X++;
Y++;
}
static void Main(){
Program p = new Program();
p.IncrementFields();
p.X = 5;
Console.WriteLine(“P.X:”+p.X+” p.Y:”+p.Y);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
其他预定义特性
特性 意义
CLSCompliant 声明可公开的成员应该被编译器检查是否符合CLS。兼容的程序集可以被任何.NET兼容的语言使用
Serializable 声明结构可以被序列化
NonSerialized 声明结构不可以被序列化
DLLImport 声明是非托管代码实现的
WebMethod 声明方法应该被作为XML Web服务的一部分暴露
AttributeUsage 声明特性能应用到什么类型的程序结构。将这个特性应用到特性声明上
多个特性
我们可以为单个结构应用多个特性。有下面两种添加方式
独立的特性片段相互叠在一起
[Serializable]
[MyAttribute(“Simple class”,”Version 3.57″)]
单个特性片段,特性之间使用逗号间隔
[Serializable,MyAttribute(“Simple class”,”Version 3.57″)]
全局特性
我们可以通过使用assembly和module目标名称来使用显式目标说明符把特性设置在程序集或模块级别。
程序集级别的特性必须放置在任何命名空间之外,并且通常放置在AssemblyInfo.cs文件中
AssemblyInfo.cs文件通常包含有关公司,产品以及版权信息的元数据。
[assembly: AssemblyTitle(“ClassLibrary1”)]
[assembly: AssemblyDescription(“”)]
[assembly: AssemblyConfiguration(“”)]
[assembly: AssemblyCompany(“”)]
[assembly: AssemblyProduct(“ClassLibrary1”)]
[assembly: AssemblyCopyright(“Copyright © 2015”)]
[assembly: AssemblyTrademark(“”)]
[assembly: AssemblyCulture(“”)]
自定义特性
应用特性的语法和之前见过的其他语法很不相同。你可能会觉得特性跟结构是完全不同的类型,其实不是,特性只是某个特殊结构的类。所有的特性类都派生自System.Attribute。
声明一个特性类和声明其他类一样。有下面的注意事项
声明一个派生自System.Attribute的类
给它起一个以后缀Attribute结尾的名字
(安全起见,一般我们声明一个sealed的特性类)
特性类声明如下:
public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute : System.Attribute{
…
特性类的公共成员可以是
字段
属性
构造函数
构造函数
特性类的构造函数的声明跟普通类一样,如果不写系统会提供一个默认的,可以进行重载
构造函数的调用
[MyAttribute(“a value”)] 调用特性类的带有一个字符串的构造函数
[MyAttribute(“Version 2.3″,”Mackel”)] //调用特性类带有两个字符串的构造函数
构造函数的实参,必须是在编译期间能确定值的常量表达式
如果调用的是无参的构造函数,那么后面的()可以不写
构造函数中的位置参数和命名参数
public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute:System.Attribute{
public string Description;
public string Ver;
public string Reviewer;
public MyAttributeAttribute(string desc){
Description = desc;
}
}
//位置参数(按照构造函数中参数的位置)
//命名参数,按照属性的名字进行赋值
[MyAttribute(“An excellent class”,Reviewer = “Amy McArthur”,Ver=”3.12.3″)]
限定特性的使用
有一个很重要的预定义特性可以用来应用到自定义特性上,那就是AttributeUsage特性,我们可以使用它来限制特性使用在某个目标类型上。
例如,如果我们希望自定义特性MyAttribute只能应用到方法上,那么可以用如下形式使用AttributeUsate:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTarget.Method)]
public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute : System.Attribute{
…
AttributeUsage有是三个重要的公共属性如下:
ValidOn 保存特性能应用到的目标类型的列表,构造函数的第一个参数就是AttributeTarget 类型的枚举值
Inherited 一个布尔值,它指示特性是否会被特性类所继承 默认为true
AllowMutiple 是否可以多个特性的实例应用到一个目标上 默认为false
事件和委托的区别
之前对事件和委托的概念一直很模糊,虽然知道怎么用,但是感觉理解还不是很透彻的.
现在总算是理解了,具体总结如下.
事件:
1.是一种特殊的委托
2.它不能在方法内定义
3.它不能在所定义的类外所调用
-事件是一种特殊的委托,或者说是受限制的委托,是委托一种特殊应用,只能施加+=,-=操作符。二者本质上是一个东西。
-event ActionHandler Tick; // 编译成创建一个私有的委托示例, 和施加在其上的add, remove方法.
-event只允许用add, remove方法来操作,这导致了它不允许在类的外部被直接触发,只能在类的内部适合的时机触发。委托可以在外部被触发,但是别这么用。
-使用中,委托常用来表达回调,事件表达外发的接口。
-委托和事件支持静态方法和成员方法, delegate(void * pthis, f_ptr), 支持静态返方法时, pthis传null.支持成员方法时, pthis传被通知的对象.
-委托对象里的三个重要字段是, pthis, f_ptr, pnext, 也就是被通知对象引用, 函数指针/地址, 委托链表的下一个委托节点.
事件(event)基于委托,为委托提供了一个发布/订阅机制,我们可以说事件是一种具有特殊签名的委托。
什么是事件?
事件(Event)是类或对象向其他类或对象通知发生的事情的一种特殊签名的委托.
事件的声明
public event 委托类型 事件名;
事件使用event关键词来声明,他的返回类值是一个委托类型。
通常事件的命名,以名字+Event 作为他的名称,在编码中尽量使用规范命名,增加代码可读性。
为了更加容易理解事件,我们还是以前面的动物的示例来说明,有三只动物,猫(名叫Tom),还有两只老鼠(Jerry和Jack),当猫叫的时候,触发事件(CatShout),然后两只老鼠开始逃跑(MouseRun)。接下来用代码来实现。(设计模式-观察者模式)
正则表达式匹配
在C#中使用正则表达会大大提高开发效率.如当你要匹配一个IPV4的地址的时候
string ip4 = "192.168.1.5";//你要匹配的地址
string pattern4 = @"^((([01]?\d\d?|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5])\.){3}([01]?\d\d?|2[0-4]\d|25[0-5]))$";//匹配公式
bool isIP=Regex.IsMatch(ip4,pattern4);//判断是否匹配成功;
Console.WriteLine(isIP);
string str1 = @"^\d*$";//正则表达式表示一个数字字符串;
string str2="1s";//Console.ReadLine();
bool flag=Regex.IsMatch(str2, str1);//只要有一个符合则认为是满足的
string str3 = "how to solve the problem has become to hot issue among many people";
string pattern2=@"[^how]";
Console.WriteLine(Regex.Replace(str3,pattern2,"*"));//把str3中出现的h,o,w字符替换为*;
lambada表达式
lambada 表达式在C#里面也是一种匿名方法的表达方式.如下
Func<int, int, int> plus1 = (a, b) =>//lambada表达式的参数是不需要声明类型的;
{
return a+b;
};
Console.WriteLine(plus(5,6));//输出11;
Func<int, int> pl = a => a + 1;//当参数只有一个的时候可以不用括号,当函数体中只有一行语句的时候也不需要大括号如果有返回值将自动返回这个值;
Console.WriteLine(pl(5));//输出6
通过Lambada表达式可以访问Lamdada表达式块的外部的变量,但是这个使用要很谨慎,因为变量很容易受到外部影响.
Func<int, int, int> plus =delegate(int a,int b)//匿名方法;
{
return a+b;
};
Console.WriteLine(pl(5,6));//输出11
Unity3D—UGUI学习
最近学习了一下unity3D自带的UGUI发现他和NGUI是差不多的所以学起来是很快的,基本上NGUI上有的功能在UGUI上都可以实现吧.
就像NGUI的所有的组件都是在UIROOT下的,而在UGUI中的UI组件是需要在Canvas下的.否则是看不见他们的.在UIroot中是有一个相机的组件的然后专门用来渲染UI组件的可以调整相机的属性达到不同的效果,而在UGUI中却没有这么一个相机组件,但是它可以在Canvas的RenderMode属性中设置渲染的方式,达到UI的显示方式,比如使UI贴在屏幕中不动或跟着摄像机移动或者是转换成3D视角方式显示UI.
不同的是 在NGUI中UIROOT只能有一个,而UGUI中的Canvas可以有多个并不限制.
两者的按钮响应事件的添加方式是类似的,都是直接拖动物体到OnClick属性中,然后选择对应的函数.
而在NGUI中某些事件的响应可以通过添加它自带的脚本实现,但是在UGUI中是通过在自己创建的脚本中继承某些接口然后实现它的函数来达到效果的.
比如在UGUI中通过继承IBeginDragHandler,IEndDragHandler,IDragHandler,IPointerEnterHandler等接口来实现鼠标的拖拽功能,和鼠标的移入移出等事件的捕获.然后实现如下函数.